NFTs have blown up in the last couple of years, hitting $20 billion dollar market cap. People are spending millions of dollars on NFTs. NFT Marketplaces and companies are popping up all over the place, scams run rampant, and overall this whole NFT thing is pretty crazy.
If you’re new to the world of NFTs and you literally have no idea how they work, welcome. This guide is going to walk you through everything you need to know. Once you have ventured through this post, you’ll finally be able to explain NFTs to your mom with ease.
What We Cover:
- What is an NFT
- What does NFT mean
- Benefits of NFTs
- How do NFTs work
- What does owning and NFT mean
- What’s the point of NFTs
- Why would someone buy an NFT
- Are NFTs environmentally friendly
- How NFTs are different than cryptocurrency
- Can you buy NFTs with cryptocurrency
- How do you buy NFTs
- Types of NFTs
- Popular examples of NFTs
- What are NFTs used for
- NFTs and Defi
- Should you buy NFTS
- Are NFTs important
- Are NFTs safe
- How to make an NFT
Key Info About NFTS
So what is an NFT?
An NFT is a unique digital asset. No two NFTs are exactly the same. They all have different addresses on the blockchain that was used to create the NFT. Most NFTs are minted on Ethereum, Polygon, and Solana.
NFTs come in many shapes and sizes. Right now, a lot of NFTs are just pictures and artworks. There are other things that are NFTs too like music, videos, video game items, and more. Technically, anything can be turned into an NFT.
Most NFTs are purely digital, meaning they aren’t tied to any kind of physical object or asset, although that might change in the near future. Some people think you will be able to buy a house as an NFT one day.
What does NFT mean?
NFT stands for Non-Fungible Token. This basically means that no two NFTs are of exact interchangeable value (like money). They are also a token, which represents perceived value. Let’s break this down some more to make it easier to understand.
Non-fungible vs Fungible

The key difference between a fungible token and a non-fungible token is that a non-fungible token can’t be exchanged for the exact same value. For example, a $10 bill can be exchanged for a different $10 bill. Those bills are fungible tokens. If two brand new coats that are exactly the same can be exchanged, then they have the exact same value they are fungible.
Fungible Meaning
Fungible literally means a product or good that is mutually interchangeable. Money is fungible.
Non-Fungible Explained
A non-fungible token is unique. For example, let’s say you have two footballs. They are exactly the same but one is signed by your favorite NFL player. The signed football is unique and can’t be exchanged for a similar unsigned football. It has a unique attribute that makes it valuable. Its’s non-fungible.
Non-fungible tokens are similar. They have unique addresses that can be verified on a blockchain. Their authenticity can be proven, and you can’t fake them. Even two NFT images that are the same will have different addresses to make them distinguishable.
Benefits of NFTs
The key features making NFT such popular technology are:
- proof of ownership – The information about the creator is permanently stored on the blockchain it is minted on. Any time you buy or sell an NFT, it can be easily proved who owns it by looking at the metatada of transactions. The creator also has all authorship rights and can set royalties on every transaction.
- uniqueness – Non-Fungible Tokens are 100% unique. Every token get’s a unique address. No two are the same. The fact that they are totally unique makes it impossible to create counterfeit NFTs and prevents fraud issues.
- transparency – NFT transactions are public records. You can view the transaction history of the NFT within the metatada of the blockchain records. There is some unanimity within the wallets being used to transact. However, if you know who owns said wallet address you will be able to see all their trades.
- investment potential – NFTs offer a big potential upside for interested investors. The value of NFTs can skyrocket and plummet in short timeframes. It’s a very volatile market. But investors who have a high-risk tolerance and make smart moves are able to make much faster gains with NFTs compared to just buying and selling coins.
How do NFTs work?
NFTs are created (minted) on a blockchain (like Ethereum) and then they can be collected, bought, sold, or transferred to a digital wallet. In the crypto world, everyone has digital wallets to hold their cryptocurrencies and NFTs.
If you own an NFT you can sell it on an NFT marketplace (like OpenSea). You can set a listing price for your NFT and when someone buys it you will get cryptocurrency in exchange for your NFT.
However, this isn’t the only use case for NFTs. Here’s another one. There’s a popular NFT game called AxieInfinity. In this game, you collect cute axolotl NFTs (Axies). You can also buy items and land in the game. Every item in the game is an NFT that can be bought and sold on their marketplace or even a third-party marketplace. Surprisingly, over $4 billion US dollars have been exchanged for Axie NFTs.
Holding onto a specific NFT can also get you access to perks like exclusive memberships, giveaways, cryptocurrencies, and more.
There are a lot more use cases for NFTs. Later in this post, we will explore some of the most popular examples of how NFTs work.
What does owning an NFT mean?
When you own an NFT, it means you currently possess an NFT in one of your crypto wallets. When you own an NFT you get to decide what to do with it. You can keep it forever, destroy it, sell it, etc. It’s totally up to you.
When you mint or buy an NFT you need to connect your wallet so that the unique address of your NFT can be sent to that wallet. The unique address is the key part of NFT ownership. This magical code in your wallet is proof that you own that specific NFT. Records on blockchains are public (ledger), so it’s easy for people to see that the NFT was transferred to your wallet.
When someone checks on an NFT, they can see that its most recent transaction was sending it to your wallet, and it hasn’t moved since. This indicates that you’re holding your NFT. If you one day sell or transfer your NFT somewhere else, people can see that too.
What’s the point of NFTs?
When people are new to NFTs they see the million-dollar monkey Jpegs and think the whole thing is just pretty dumb. The current state of NFTs gives a bad impression. The truth is that NFT technology is a game-changer. The expensive monkey pictures are just the beginning. Profile picture NFTs like the Bored Ape Yacht Club collection were pretty much just the first use case for NFTs. The NFT industry is already moving towards NFTs that have real use cases that provide value and solve problems.
The big reason why people like NFTs is that they allow people to buy and sell digital goods with cryptocurrency. Before NFTs, all you could really do with cryptocurrency was buy and sell different coins. NFTs are great for cryptocurrency because adoption in real life is moving slowly. You can’t walk into your favorite stores and pay for stuff with bitcoin yet.
NFTs also bring real value to digital assets. This is opening doors for innovators to come up with creative ideas to use NFT technology in their industries. We’re seeing NFT adoption quickly evolving in art, gaming, music, fashion, digital real estate, the metaverse, and more.
NFTs are actually solving a lot of painful problems in industries that have been stagnant for years.
For example, the online event ticketing industry is about to be disrupted by NFTs. This is an industry expected to be valued at around 94 billion by 2027. NFT ticketing solves problems like lost revenue from a lack of resale control and can totally prevent ticket fraud.
One of the fasted moving NFT markets right now is video games. NFT gaming allows players to earn NFTs by playing, which can then be sold on marketplaces and even exchanged for cryptocurrency and fiat money. Before NFTs were introduced to video games you would only be able to buy and sell items if there was a built-in marketplace in a game. NFT gaming introduces a dynamic market system where you can buy and sell on a variety of third-party marketplaces for the same game.
Key Talking points About NFTS:
Why would someone buy an NFT when you can just copy/paste it for free?
This is a common question people wonder when first learning about NFTS. If an NFT is just an image, what’s stopping people from just copy/pasting it somewhere else and claiming they own it? If you’re wondering the same thing, you’re likely trying to figure out how other people are able to see massive value in an NFT, spending thousands or sometimes even millions of dollars on them.
While this is a valid point, you can definitely download a picture of an NFT and claim you own it, but you won’t be able to prove you own it. The thing that gives NFTs their value Is the fact that they have a unique address within a blockchain, and that address can be tracked from the NFTs creation (minting) to every sale, transfer, and resale, ever.
For example, Twitter founder Jack Dorsey recently sold his first tweet as an NFT for $3 million dollars. Then this famous NFT recently made headlines again when it was relisted on a marketplace and was being bid on for thousands, not millions, of dollars. Indicating a massive drop in the value of the NFT.
If you go on OpenSea and look for Jack Dorsey’s tweet, you’ll actually have a hard time finding it. There are tons of people claiming to be selling it, there is only one real one. This real NFT can be traced back to its origin by following its unique address.
Are NFTs environmentally friendly?
A very common topic that the media likes to talk about is how NFTs aren’t environmentally friendly due to the high electricity costs of blockchain transactions. Let’s explore this a bit.
The reasoning behind this claim is that the computers used to mine coins like Ethereum consume a lot of electricity. And because of the rising popularity of cryptocurrency and NFTs, there are a lot more transactions going on, which leads to more energy consumption.
Every time an NFT is bought, sold, created, or transferred, it creates a transaction that consumes electricity on a mining machine to facilitate.
In fact, there are entire football-field-sized warehouses dedicated to mining cryptocurrency called crypto farms.
That’s where most people stop learning about this issue. However, there is a lot going on behind the scenes to resolve the energy problem of cryptocurrency.
The high energy cost of cryptocurrency transactions is one of the most painful issues for crypto users, especially in the NFT space. Because people who are making transactions are also paying fees to miners for facilitating transactions, which is how miners make money. Increased demand for transactions increases the fees paid (gas).
However, the high gas fees combined with high electricity consumption means it’s one of the biggest opportunities for innovators to step in. And it’s already happening. Solutions are being created to make transactions faster, cheaper, more energy-efficient, and sometimes even free.
Ethereum is working on Ethereum 2.0, which will consume far less electricity. The gas problem also created solutions like Polygon and Immutable X, which are layer-2 scaling solutions that make transactions faster, easier, and cheaper.
So while there is a lot of energy consumption in the crypto and NFT market today, this is seen as a big opportunity by innovators around the world to find energy-efficient solutions. So this won’t always be the case.
NFTs and crypto
How are NFTs different from cryptocurrency?
The big difference between cryptocurrency and NFTS is that Cryptocurrency is basically digital money, while NFTs are things you can buy with your digital money. They both live on the same blockchain though.
For example, if an NFT is minted on the Ethereum blockchain, you will need to use Ethereum to buy or sell that NFT. NFT transactions are stored within the code of the blockchain in the same way that coins are held.
Can you buy NFTs with cryptocurrencies?
Yes! In most cases, cryptocurrency is the only thing you can buy an NFT with. That’s because NFTs are minted on a cryptocurrency’s blockchain. Due to the way that blockchain technology works, You will need to buy and sell an NFT with the same cryptocurrency that the NFT is minted on.
If you don’t have the type of cryptocurrency needed to purchase a specific NFT you can convert fiat money (regular $) into cryptocurrency, or you can exchange one type of cryptocurrency for another. Most crypto exchanges and even some wallets offer features for swapping and exchanging currencies.
How do you buy NFTs?
In order to buy NFTs, you will need two things, a crypto wallet, and cryptocurrency. You will need the right type of currency for the NFT you want to buy.
In order to fund your wallet with cryptocurrency, you will need to join a crypto exchange like Coinbase or Binance, there are lots out there, but those are just two of the most well-known ones. Once you have signed up on that exchange you can convert your regular fiat money to cryptocurrency. How much crypto you get for your money depends on the value of that coin compared to your fiat currency.
Once you have funded a crypto wallet with cryptocurrency from your crypto exchange account, you’re ready to go to an NFT marketplace to buy an NFT. One of the most popular ones is OpenSea, which has a massive selection of Ethereum NFTs. They also have Polygon, Solana, and Klaytn NFTs.
NFT examples and use cases
Types of NFTs
The most popular types of NFTs are currently art-based. Art NFTs are mainly profile picture NFTs, meaning the main use case is to use your NFT as a profile picture. And other art NFTs that aren’t for profile pictures are just digital art, with the added benefit of owning it.
However, this isn’t the only type of NFT. Even though NFTs are still pretty new, there is a wide variety of NFTs like music NFTs, gaming NFTs, NFT tickets, NFT videos, NFT real estate, etc.
In the sports world, NFTs are being created to commemorate events, moments, and players. Kind of like digital trading cards.
There are endless use cases for NFTs. Anything digital can easily be turned into an NFT simply by minting it on a blockchain. It’s a little trickier to turn something physical like a pair of shoes into a non-fungible token but not at all impossible. Items you buy in the near future may even come with a digital twin item as an NFT that you might be able to use on a personal avatar.
For physical use cases, an NFT would simply be the digital representation of that physical item. Experts have even claimed that one day you will be able to buy houses as an NFT.
Examples of popular NFTs
Some of the most famous and popular NFTs are the ones that are worth the most money. Let’s explore a couple of them.
Beeple’s Everydays – The First 5,000 Days

Beeple’s iconic NFT sold for $69 million dollars. This is currently the single highest value NFT ever purchased. This was a single NFT composed of the artist’s first 5,000 days of making an artwork every single day.
The record-breaking sale made Beeple one of the top three most valuable living artists. This NFT is probably one of the most well-known and frequently mentioned due to its massive sale price.
This popular NFT signaled to the world that it was now entirely possible to sell high-value digital art, which has opened doors and inspired many artists and collectors to get into the NFT craze.
Bored Ape Yacht Club
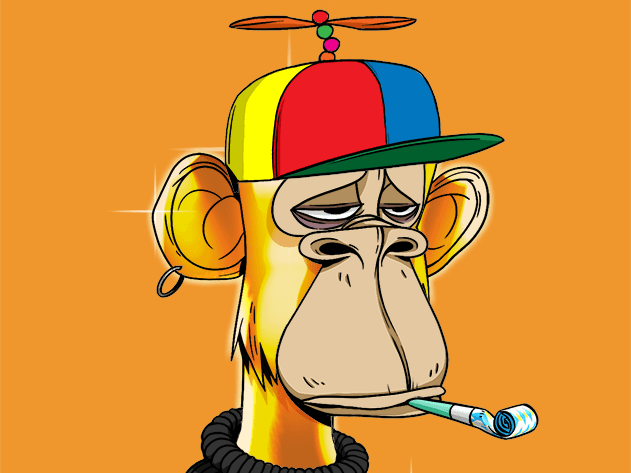

Bored Apes were one of the first NFT collections to strike it big. These NFTs sell for millions of dollars today. In total, the Bored Ape Yacht Club collection of 10,000 ape NFTs has transacted over $1.87 billion dollars in sales.
This collection of Ethereum NFTs features monkeys with bored expressions with randomized traits to make them unique. Owning one also gets you access to the exclusive club on discord, where other Bored Ape owners hang out and chat.
Many celebrities and high-net-worth individuals own a Bored Ape, so just by owning one, you get to network with some really awesome people.
Owning a Bored Ape NFT also grants you access to other perks like free Mutant Apes and Kennel Club NFTs.
Cryptopunks

CryptoPunks are one of the most well-known NFT collections. A single Cryptopunk sells for hundreds of thousands of dollars. But they weren’t always like that.
In fact, Cryptopunks was one of the very first NFT collections. Back in 2016, they were given away to anyone who was willing to cover the gas fee to mint one.
After years of gaining traction, the Cryptopunks managed to gain their celebrity status. Today Icons like this celebrity and that rich guy don their glistening CryptoPunks as a way to flex their expensive jpegs.
Twitter Founder Jack Dorsey’s first tweet
Jack Dorsey turned his first-ever Tweet into an NFT and sold it for $2.9 million to crypto entrepreneur Sina Estavi in March 2021. This sparked media attention for the NFT industry. Later in April 2022 Sina relisted the NFT for $49 million and received a whopping top bid of $280.
The lack of offers gained media attention again, which made people wonder if there was something wrong with NFTs. Many media outlets used this to make a case that NFTs are bad, or not worth the money.
However, the NFT market is still growing and expanding. The fact that no one wants to spend $49 million dollars on a picture of a tweet doesn’t affect the NFT industry as a whole. Currently, the highest offer for the tweet is just over $20k.
Where to buy: If you’re interested in checking out the bids for the official Jack Dorsey Tweet NFT, check it out on OpenSea listed by SinaEstavi.
What are NFTs used for?
NFTs have a variety and growing list of use cases. Non-Fungible tokens started out being used to buy and sell art. The most popular type of NFT is are profile pictures, or PFPs. Popular NFTs like crypto punks and bored apes are PFP NFTs.
NFTs are also being quickly adopted by the gaming industry. The use case for gaming NFTs is awesome. Gaming NFTs allow players to buy and sell items, characters, and virtual land within their favorite games. And most of the time these NFTs can be sold on any marketplace that accepts the cryptocurrency the NFT is minted on.
Another big use case for NFTs in the metaverse. Similar to gaming, you can buy and sell items, characters, and land. However, the metaverse has other applications beyond just playing games such as virtual reality, meetings, chat rooms, etc.
NFTs are also being adopted by the ticketing industry. NFT ticketing solves some of the biggest problems in the ticketing space. Events that sell tickets face issues with fraud and resellers buying out all the tickets and selling them at much higher prices. NFT ticketing allows events to prevent fraud with unique NFT tickets, as well as collect revenue from ticket resales through smart contracts.
NFTs are also being adopted in music, sports, photography, and more. Because NFTs allow people to buy and sell virtual and physical items on a blockchain, the use cases for NFT technology are vast.
NFTs and Defi
NFTs have even more use cases when you look at Decentralized Finance (DeFi). In short, Defi is all about using blockchain technology and cryptocurrency to do all the stuff that banks, governments, and big financial companies do with money.
Innovators are building Defi platforms for loans, insurance, banking, and more. And bringing NFT technology into the space expands its capabilities.
NFTs and Defi is a much larger topic, but here are some quick NFT Defi use cases:
- Using a valuable NFT as automated collateral on a loan
- Fractionalizing an NFT and buying/selling little pieces of it
- Turning finance and insurance contracts into NFTs to automate boring paperwork
- Lending valuable NFTs for a small fee
NFTs and investing
Please be aware that this blog does not constitute as financial advice.
Should you buy NFTs?
Ultimately, that’s up to you. Many people buy NFTs thinking they will all dramatically increase in value because they are NFTs and NFTs are super cool and popular. However, that’s not the case.
NFTs are realistically a high-risk investment. Even more so than cryptocurrency. That’s because the value of the cryptocurrency they are minted on can increase and decrease on any given day, and so can the value of the NFT you want to buy or sell.
That being said, it does not necessarily mean that NFTs are bad investments. Similar to stocks and crypto, if you know how to invest and take calculated risks, NFTs can be rewarding.
If you don’t want to buy NFTs there are still other ways to invest in the NFT market. For example, you could buy coins from NFT marketplaces like SuperRare or Rarible. You could buy stocks for companies getting into NFTs like DraftKings or Gamestop, or even blockchain scaling solutions that are heavily involved in NFT projects like Polygon or Immutable X.
You could even invest in NFT projects, or start your own.
Are NFTs important?
Yes, NFTs are indeed important. NFTs represents the first time in history that people have been able to buy and sell, and own digital goods at scale. NFTs are essentially smart contracts that have proof of ownership, transparency, security, and even royalties built into them.
The technology behind NFTs has the capability to change the way people buy and sell things online. Not just for digital goods, but also for physical goods.
Are NFTs safe?
The technology behind NFTs is safe, but that doesn’t mean it’s totally risk-free. There have been plenty of NFT rug pulls (scams) as well as reports of hackers, thieves, and even dark web usage.
From a technology perspective, NFTs are just as risky as crypto.
Another element that makes NFTs risky is how easy it can be to lose your money. For example, you could invest a large sum of ETH into an NFT and the value of it could plummet the next week.
However, if you know how to manage cryptocurrency and make smart decisions, NFTs can be rewarding to purchase. NFTs have big upside potential and big downside potential. Many people even buy NFTs just to participate in closed online communities only available to holders of specific NFTs. If you own a Bored Ape or a CryptoPunk, you get to join their discord channels full of celebrities, entrepreneurs, and NFT enthusiasts.
How to make an NFT
Making an NFT is fairly simple. You need a platform that allows minting. Then you’ll need some cryptocurrency, and a digital good like an image, video, or audio recording.
You then mint your NFT on that platform, pay the minting fees, and list your item for sale on the marketplace.
In some cases, you can make an NFT by minting from a collection that is currently being minted. This basically means that you pay the collection creators to automatically generate your own unique NFT.
There is obviously a bit more to it than that, but that’s the five-second summary of how it works. Here are some useful guides for making NFTs on some of the most popular marketplaces.
Conclusion
Hopefully, this article has helped you understand what NFTs are and how they work. In summary, NFTs are great and you shouldn’t pass up on this exciting opportunity to participate in the next phase of the web. Also known as web 3.0.

